属性上报预处理规则
属性上报预处理规则
提示
如果您还不了解什么是 ThingsCloud 消息规则,以及消息规则的创建方法,请浏览 消息规则基础。
属性上报预处理规则的触发时间,是在云平台接收到硬件设备的属性上报,且在正式更新设备属性之前。属性上报预处理规则用于对设备上报属性做必要的格式处理、二次计算、转化、合并等,总之可以进行任意的加工。
属性上报预处理规则支持的操作如下:
- 预处理函数
- GPS 位置坐标系转换
- GPS 位置电子围栏检查(圆形)
- GPS 位置电子围栏检查(多边形)
- 计算抄表周期累计值
如下图:
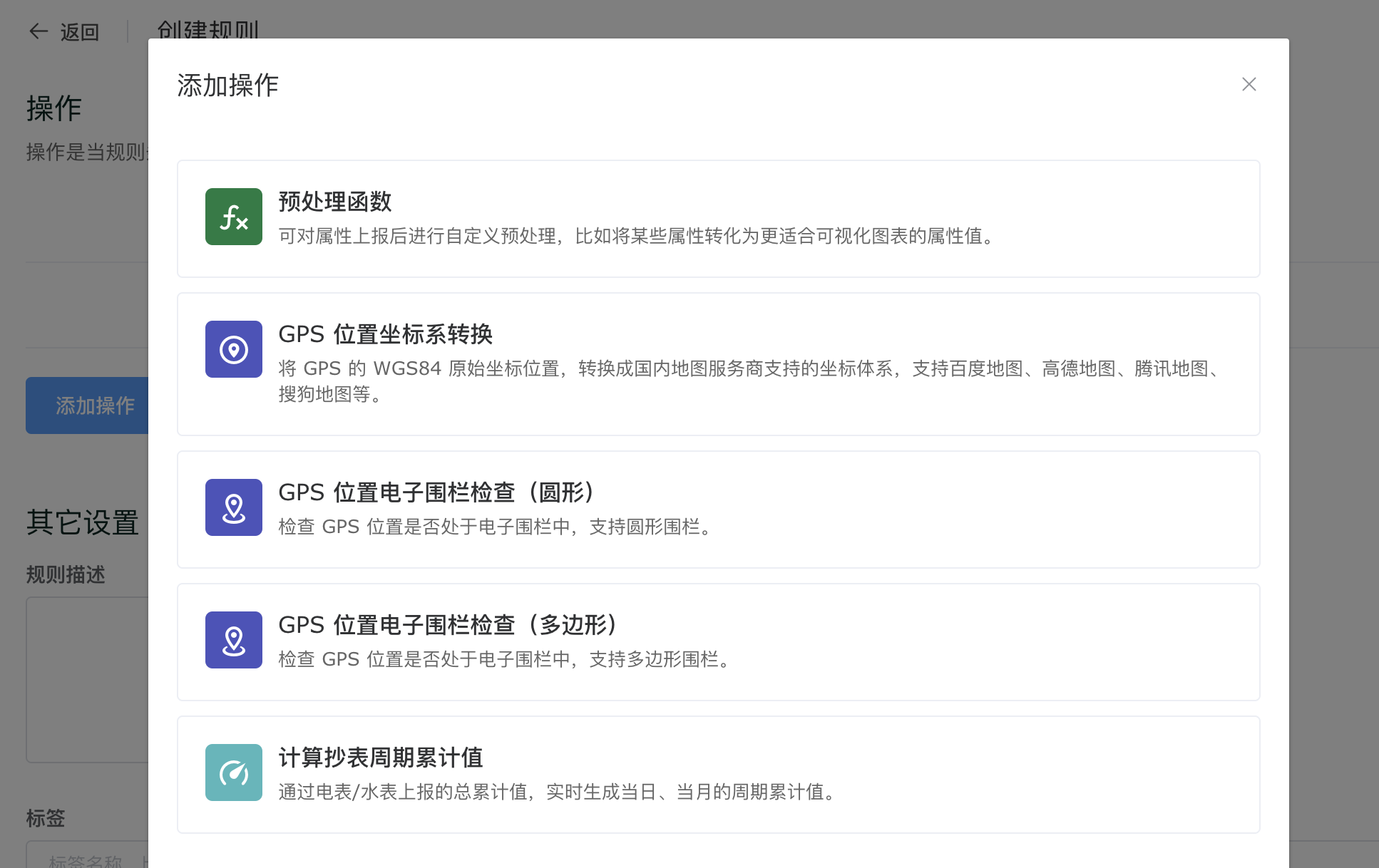
预处理函数
使用预处理函数操作,您可以根据需要来编写相应的云函数,对设备上报的属性做任意的处理,处理结果必须符合属性上报的规范。
云函数使用 Javascript 编程语言,以下是默认的属性上报预处理函数,您需要添加自己的函数代码。
module.exports = function (report_attributes) {
/**
* report_attributes: 上报的属性对象,同时作为函数返回值。函数中可操作属性对象。
*/
return report_attributes;
}
提示
当您在消息规则中编辑云函数时,可以多多使用在线调试功能,帮助您验证代码的准确性,并提升开发速度。详细介绍请浏览:每日调用上亿次的消息规则云函数,如何在线测试?。
示例:对设备上报的属性值做一些计算处理
这是一个最简单的例子,帮助您快速了解属性上报预处理的工作机制。
我们需要对设备上报的 temperature 温度属性值乘一个固定的系数 0.1,编写预处理函数如下:
module.exports = function (report_attributes) {
/**
* report_attributes: 上报的属性对象,同时作为函数返回值。函数中可操作属性对象。
*/
if (report_attributes.temperature !== undefined) {
report_attributes.temperature = report_attributes.temperature * 0.1;
}
return report_attributes;
}
当设备上报属性为:
{
"temperature": 261
}
经过以上规则预处理后,设备上报的消息实际上变成了:
{
"temperature": 26.1
}
示例:对设备上报的温湿度计算生成温热指数(THI)
温热指数(temperature-humidity index,THI),又称不适指标。通常用来形容畜禽养殖过程中是否处于热应激状态及其程度,是最经典的评价动物热应激状态的指标。
可以使用属性上报预处理函数,对传感器上报的温度和湿度进行实时计算,云函数如下:
module.exports = function (report_attributes) {
/**
* report_attributes: 上报的属性对象,同时作为函数返回值。函数中可更新属性对象。
*/
if (report_attributes.temperature !== undefined && report_attributes.humidity !== undefined) {
var t = report_attributes.temperature;
var h = report_attributes.humidity;
report_attributes.THI = (1.8*t+32)-(0.55-0.55*h*0.01)*(1.8*t-26);
}
return report_attributes;
}
更多关于生成 THI 的介绍,请浏览 通过温湿度自动生成温热指数(THI)。
示例:根据电池电压计算电池剩余容量
设备定时上报电池的原始电压值,根据电池手册中容量的计算方法,我们可以写出以下的预处理函数:
module.exports = function (report_attributes) {
/**
* report_attributes: 上报的属性对象,同时作为函数返回值。函数中可操作属性对象。
*/
if (report_attributes.volt !== undefined) {
report_attributes.battery = (report_attributes.volt - 3.6) / 0.4 * 100;
}
return report_attributes;
}
以上函数中,判断设备上报的 volt 属性如果存在,则通过计算,生成一个新的属性 battery 表示电池电量百分比。
示例:记录属性上报次数
假设我们要记录设备上报湿度 humidity 的次数,可以写一个这样的预处理函数,生成 humidity_count 这个属性,统计湿度属性的总上报次数。
module.exports = function (report_attributes) {
if (report_attributes.humidity !== undefined) {
// 读取设备当前的属性
var curr_attrs = Cloud.getCurrentAttributes();
if (curr_attrs.humidity_count === undefined) {
// 上次计数count不存在,说明是首次上报
report_attributes.humidity_count = 1;
} else {
// 上次计数存在,本次计数+1
report_attributes.humidity_count = curr_attrs.humidity_count + 1;
}
}
return report_attributes;
}
以上函数通过使用 JavaScript 的 || 运算符,还可以进一步简化为:
module.exports = function (report_attributes) {
if (report_attributes.humidity !== undefined) {
// 读取设备当前的属性
var curr_attrs = Cloud.getCurrentAttributes();
// 本次计数+1,上次计数如果不存在则默认为0
report_attributes.humidity_count = (curr_attrs.humidity_count || 0) + 1;
}
return report_attributes;
}
在此基础上,还可以改为只统计当日的上报次数,或者计算当日的湿度平均值,思考一下如何实现呢?
示例:记录属性今日上报次数
这个例子中,通过属性上报预处理规则,生成 humidity_count 这个属性,统计湿度属性在当日的上报次数。
module.exports = function (report_attributes) {
if (report_attributes.humidity !== undefined) {
// 读取设备当前的属性
var curr_attrs = Cloud.getCurrentAttributes();
// 读取上次的计数,如果不存在则默认为0
var humidity_count = curr_attrs.humidity_count || 0;
// 判断上一次记录的日期,如果不是今天,则清零
if (curr_attrs.humidity_date !== Cloud.Utils.dateFormat("YYYY-MM-DD")) {
humidity_count = 0;
}
// 本次计数+1
report_attributes.humidity_count = humidity_count + 1;
// 记录今天日期
report_attributes.humidity_date = Cloud.Utils.dateFormat("YYYY-MM-DD");
}
return report_attributes;
}
示例:记录设备属性上报的最后更新时间
假设我们希望在控制台或者用户 App 中,直观的显示设备最后一次上报属性的日期时间,可以通过以下的属性上报预处理函数,生成一个新的属性 last_update_time 保存日期时间,您可以将这个属性放在 ThingsX App 的设备界面上。
这里会用到另一个内置函数 Cloud.Utils.dateFormat。
module.exports = function (report_attributes) {
report_attributes.last_update_time = Cloud.Utils.dateFormat("YYYY-MM-DD HH:mm:ss");
return report_attributes;
}
如果我们的需求更进一步,希望记录湿度上报的最后更新时间,修改一下如下:
module.exports = function (report_attributes) {
if (report_attributes.humidity !== undefined) {
report_attributes.last_update_time = Cloud.Utils.dateFormat("YYYY-MM-DD HH:mm:ss");
}
return report_attributes;
}
ThingsCloud 还支持完善的时区设置,假设这里使用 美国东部时区 来生成日期时间,修改如下:
module.exports = function (report_attributes) {
// 在函数开头设置时区
Cloud.Utils.setTimezone("America/New_York");
report_attributes.last_update_time = Cloud.Utils.dateFormat("YYYY-MM-DD HH:mm:ss");
return report_attributes;
}
示例:从设备上报的 base64 格式属性中提取数据
以下是设备上报的属性 JSON,其中 data 属性是 LoRaWAN 设备上报的 base64 格式数据,设备将二进制数据编码为 base64 文本格式便于发送。
{
"data": "A2fnAARoUgV9QAIGc/on"
}
通过以下属性上报预处理函数,将设备上报的 base64 格式数据解码为二进制数据,并提取其中的温度、湿度、CO2 浓度、气压等数据。
module.exports = function (report_attributes) {
/**
* report_attributes: 上报的属性对象,同时作为函数返回值。函数中可更新属性对象。
*/
if (report_attributes.data !== undefined) {
// 利用内置函数,将 LoRaWAN 设备上报的 base64 格式的 data 转为二进制数据。
var buffer = Cloud.Utils.base64ToBuffer(report_attributes.data);
// 转成 hex 格式,仅做调试记录
report_attributes.data_hex = buffer.toString('hex');
// 根据设备协议解码
let i = 0;
if (buffer[i] == 0x01 && buffer[i+1] == 0x75) {
report_attributes.battery = buffer.readInt8(i+2);
i += 3;
}
if (buffer[i] == 0x03 && buffer[i+1] == 0x67) {
report_attributes.temperature = buffer.readInt16LE(i+2) / 10;
i += 4;
}
if (buffer[i] == 0x04 && buffer[i+1] == 0x68) {
report_attributes.humidity = buffer.readInt8(i+2) / 2;
i += 3;
}
if (buffer[i] == 0x05 && buffer[i+1] == 0x7d) {
report_attributes.co2 = buffer.readUInt16LE(i+2);
i += 4;
}
if (buffer[i] == 0x06 && buffer[i+1] == 0x73) {
report_attributes.pressure = buffer.readInt16LE(i+2) / 10;
i += 4;
}
}
return report_attributes;
}
以上规则生效后,设备上报属性经过消息规则计算后,会追加新的字段 data_hex,以及提取出的传感器数据字段,如下:
{
"data": "A2fnAARoUgV9QAIGc/on",
"data_hex": "0367e700046852057d40020673fa27",
"temperature": 23.1,
"humidity": 41,
"co2": 576,
"pressure": 1023
}
详细介绍请浏览 星纵 LoRaWAN EM500 CO2 传感器上报数据解析。
示例:为风向传感器生成风向名称
风向传感器的属性上报 JSON 中,wind_direction 属性用于表示风向的角度值,范围为 0 到 360 度,0 表示正北,90 表示正东,180 表示正南,270 表示正西。
我们需要生成风向名称属性,用于在看板和 APP 中展示。编写以下属性上报预处理函数:
module.exports = function (report_attributes) {
/**
* report_attributes: 上报的属性对象,同时作为函数返回值。函数中可更新属性对象。
*/
if (report_attributes.wind_direction !== undefined) {
if (report_attributes.wind_direction >= 340) {
report_attributes.wind_direction_text = '北风';
} else if (report_attributes.wind_direction >= 295) {
report_attributes.wind_direction_text = '西北风';
} else if (report_attributes.wind_direction >= 250) {
report_attributes.wind_direction_text = '西风';
} else if (report_attributes.wind_direction >= 205) {
report_attributes.wind_direction_text = '西南风';
} else if (report_attributes.wind_direction >= 160) {
report_attributes.wind_direction_text = '南风';
} else if (report_attributes.wind_direction >= 115) {
report_attributes.wind_direction_text = '东南风';
} else if (report_attributes.wind_direction >= 70) {
report_attributes.wind_direction_text = '东风';
} else if (report_attributes.wind_direction >= 25) {
report_attributes.wind_direction_text = '东北风';
} else if (report_attributes.wind_direction >= 0) {
report_attributes.wind_direction_text = '北风';
}
}
return report_attributes;
}
详细介绍请浏览 最佳实践 · 用好属性上报预处理规则,为风向传感器生成风向名称。
示例:从键值对类型属性中提取数据
设备上报的属性 JSON 如下:
{
"dev_version": "V1.2.4",
"type": "BL101",
"IMEI": "864568060000000",
"payload": {
"temperature": 18.4,
"humidity": 65.3
}
}
我们希望将 payload 键值对中每一个数据提取出来,直接存入设备属性中,那么编写属性上报预处理函数如下:
module.exports = function (report_attributes) {
// 判断 payload 属性是否存在
if (report_attributes.payload) {
// 将 payload 中的所有字段都追加到 report_attributes 属性中
Object.assign(report_attributes, report_attributes.payload);
}
return report_attributes;
}
经过该规则处理后,设备的上报的属性 JSON 会追加新的字段如下:
{
"dev_version": "V1.2.4",
"type": "BL101",
"IMEI": "864568060000000",
"payload": {
"temperature": 18.4,
"humidity": 65.3
},
"temperature": 18.4,
"humidity": 65.3
}
示例:从数组类型属性中提取数据
设备上报的属性 JSON 如下:
{
"seq": "0.35.0.0.1",
"gateway_info": [
{
"values": {
"dev_version": "V1.2.4",
"type": "BL101",
"IMEI": "864568060000000",
"Service_provider": "NULL",
"4G_status": "NULL",
"Sim_ICCID": "NULL"
}
}
],
"sensorDatas": [
{
"flag": "signal_strength",
"value": 0
},
{
"flag": "temperature",
"value": "29.0813"
},
{
"flag": "humidity",
"value": "47.3777"
}
],
"gateway_indentify": "360TEST",
"time": "1717755300"
}
我们希望将 sensorDatas 数组中每一个数据提取出来,直接存入设备属性中,那么编写属性上报预处理函数如下:
module.exports = function (report_attributes) {
// 判断 sensorDatas 属性是否存在
if (report_attributes.sensorDatas) {
// 遍历 sensorDatas 数组
report_attributes.sensorDatas.forEach( v => {
// 将数组中每个 flag 作为标识符加入设备属性中
// 这里对 value 统一转为数值(number)类型
report_attributes[v.flag] = v.value / 1;
})
}
return report_attributes;
}
经过该规则处理后,设备的上报的属性 JSON 会追加新的字段如下:
{
...
"signal_strength": 0,
"temperature": 29.0813,
"humidity": 47.3777
}
提示
预处理函数中除了可以调用 Javascript 的标准函数外,ThingsCloud 还提供了一系列的 内置函数库,增强了云函数的能力。
示例:从设备上报 GNSS 数据中提取 GPS 经纬度
设备通过 GNSS 模组获取 NMEA 0183 格式的报文,其中 GGA 是最常用的定位信息语句,包含经纬度、海拔、定位质量等。例如:
$GPGGA,082403.000,3958.3000,N,11623.4500,E,1,08,1.0,50.0,M,0.0,M,,*5B
关键字段解析:
- 082403.000:UTC 时间(时分秒。毫秒)
- 3958.3000,N:纬度(39°58.3000′北)
- 11623.4500,E:经度(116°23.4500′东)
- 1:定位质量(1 = 有效定位,0 = 无效)
- 08:使用的卫星数量
- 1.0:水平精度因子(HDOP)
- 50.0,M:海拔高度(米)
设备端对报文进行处理后,生成 JSON 格式的属性数据,上报到 ThingsCloud,如下图:
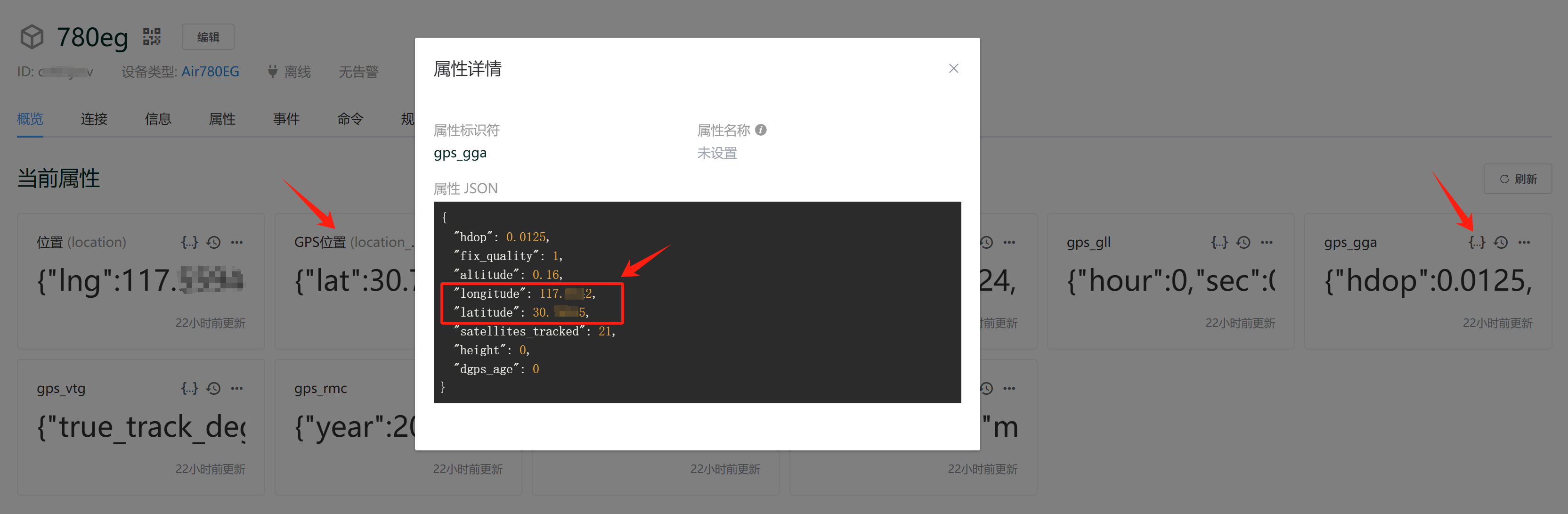
其中 gps_gga 属性是一个键值对集合,如下:
{
"gps_gga": {
"hdop": 0.0125,
"fix_quality": 1,
"altitude": 0.16,
"longitude": 111.5542,
"latitude": 32.74245,
"satellites_tracked": 21,
"height": 0,
"dgps_age": 0
}
}
我们编写以下的属性上报预处理函数:
module.exports = function (report_attributes) {
/**
* report_attributes: 上报的属性对象,同时作为函数返回值。函数中可更新属性对象。
*/
if (
report_attributes.gps_gga &&
report_attributes.gps_gga.latitude &&
report_attributes.gps_gga.longitude
) {
report_attributes.location_gps = {
lat: report_attributes.gps_gga.latitude,
lng: report_attributes.gps_gga.longitude,
};
}
return report_attributes;
};
经过该规则处理后,上报的属性消息会追加新的字段 location_gps,如下:
{
"gps_gga": {
"hdop": 0.0125,
"fix_quality": 1,
"altitude": 0.16,
"longitude": 111.5542,
"latitude": 32.74245,
"satellites_tracked": 21,
"height": 0,
"dgps_age": 0
},
"location_gps": {
"lng": 111.5542,
"lat": 32.74245
}
}
此时我们得到了一个符合位置格式的属性 location_gps,它的坐标系类型是 WGS84,可以进一步将 location_gps 属性进行[坐标系转换](#GPS 位置坐标系转换),将 WGS84 转换为 GCJ02 或 BD09,从而在 看板 或 App 面板 中展示准确的地理位置。
设备位置的更多用法,请浏览 设备位置。
更多示例
- 通过温湿度自动生成温热指数(THI)
- LoRaWAN 子设备上报数据解析示例
- 星纵 LoraWAN EM500 CO2 传感器上报数据解析
- 用好属性上报预处理规则,为风向传感器生成风向名称
- 采集型水表每日累计值计算及限量告警
GPS 位置坐标系转换
用于将 GPS 原始 WGS84 坐标转化为国内的 GCJ02(火星坐标)或 BD09(百度坐标),转化后的坐标可以在国内地图平台上正确显示位置。
在 ThingsCloud 的可视化看板中也提供了地图组件,同样经过这个坐标体系转换后,就可以显示正确的位置。如果直接显示 GPS WGS84 原始坐标,大概有几百米距离的偏移。
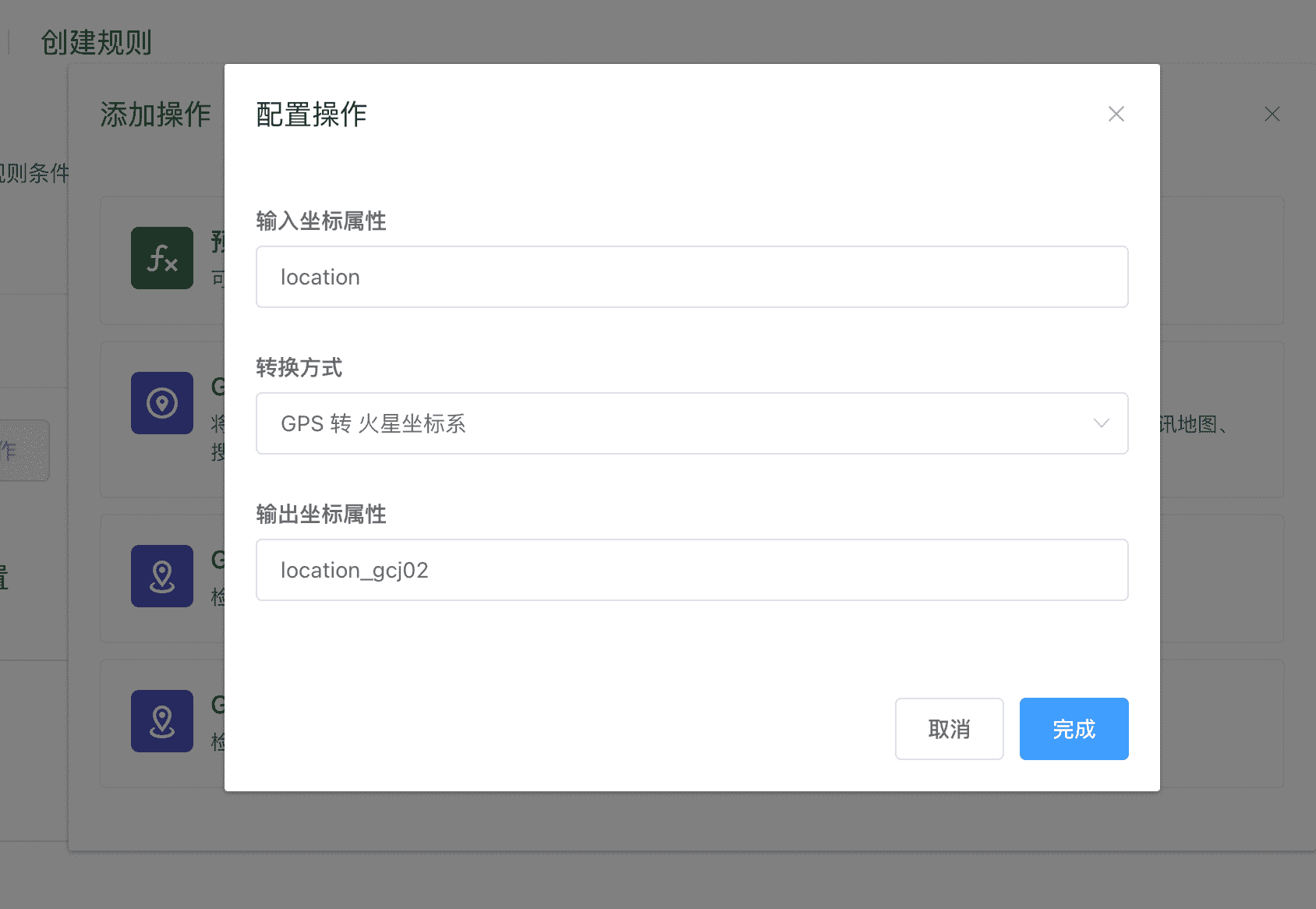
该操作需要填写以下内容:
- 输入坐标属性:填写设备上报原始 GPS 位置的属性标识符,该属性必须是
MapPoint类型。 - 转换方式:选择希望转换的目标坐标体系。
- 输出坐标属性:填写用于保存转换结果的属性标识符,该属性必须是
MapPoint类型。
如果设备所属设备类型已经创建了相应的属性功能定义,以上填写属性标识符时,会有联想提示。
GPS 位置电子围栏检查(圆形)
用于判断某个坐标位置是否处于圆形地理区域内部,实现电子围栏的功能。
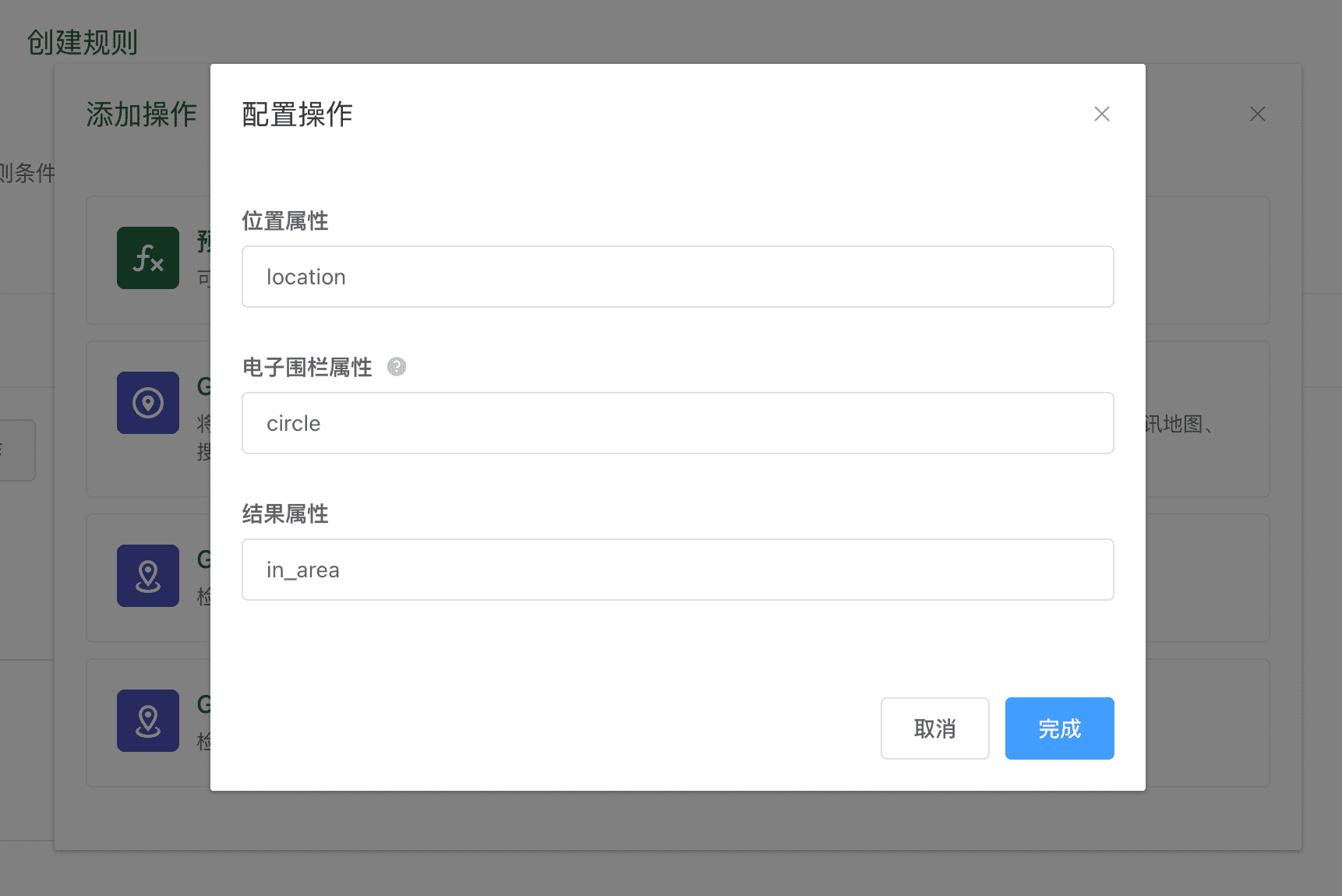
该操作需要填写以下内容:
- 位置属性:填写表示设备当前位置的属性标识符。该属性必须是
MapPoint类型。 - 电子围栏属性:填写用于保存转换结果的属性标识符。该属性必须是
MapCircle类型。 - 结果属性:填写用于保存计算结果的属性标识符,输出结果的数据类似是
Boolean,代表是否处于电子围栏内部。
如果设备所属设备类型已经创建了相应的属性功能定义,以上填写属性标识符时,会有联想提示。
GPS 位置电子围栏检查(多边形)
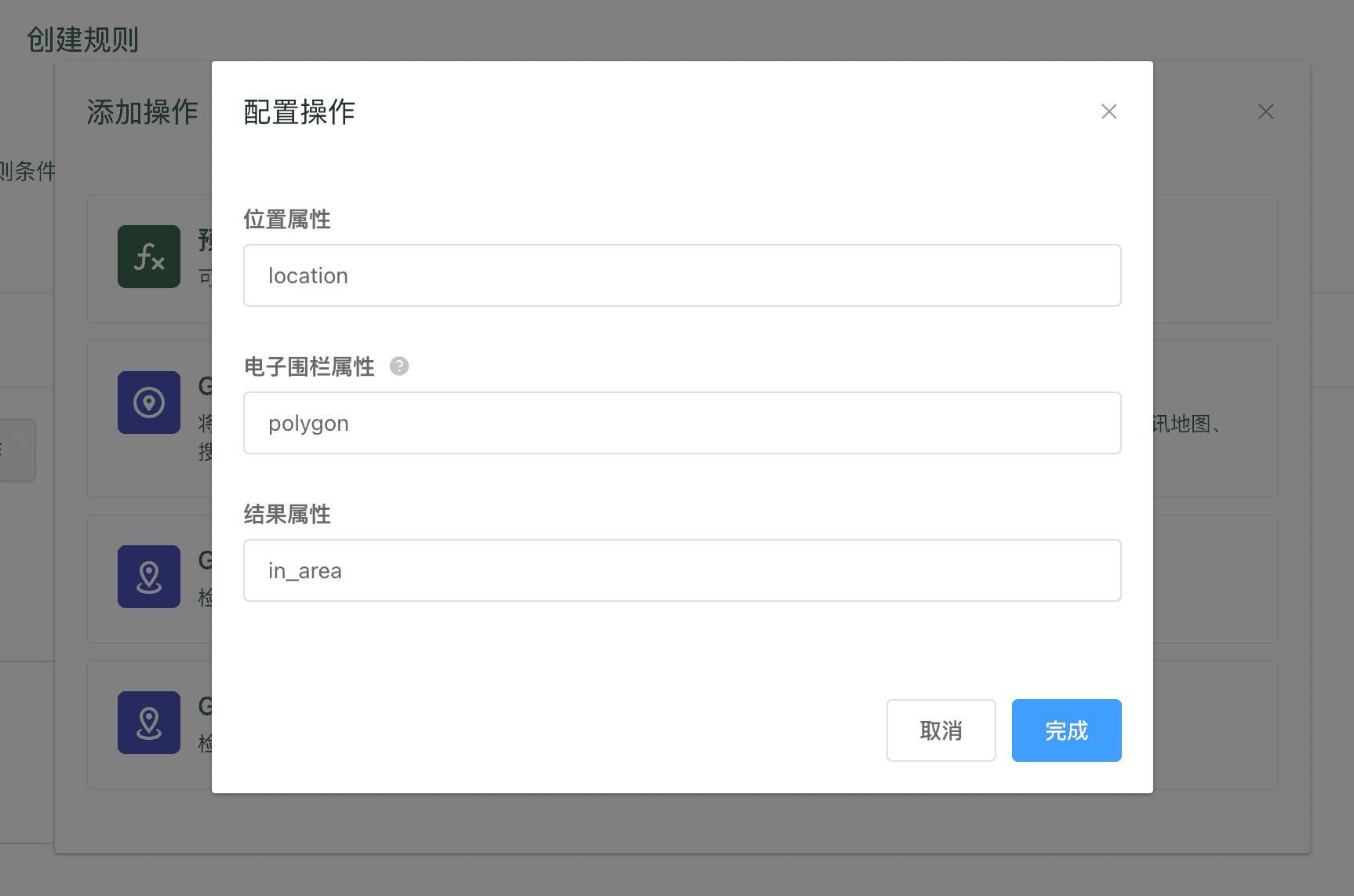
用于判断某个坐标位置是否处于多边形地理区域内部,实现电子围栏的功能。
该操作需要填写以下内容:
- 位置属性:填写表示设备当前位置的属性标识符。该属性必须是
MapPoint类型。 - 电子围栏属性:填写用于保存转换结果的属性标识符。该属性必须是
MapPolygon类型。 - 结果属性:填写用于保存计算结果的属性标识符,输出结果的数据类似是
Boolean,代表是否处于电子围栏内部。
如果设备所属设备类型已经创建了相应的属性功能定义,以上填写属性标识符时,会有联想提示。
计算抄表周期累计值
请参考:
